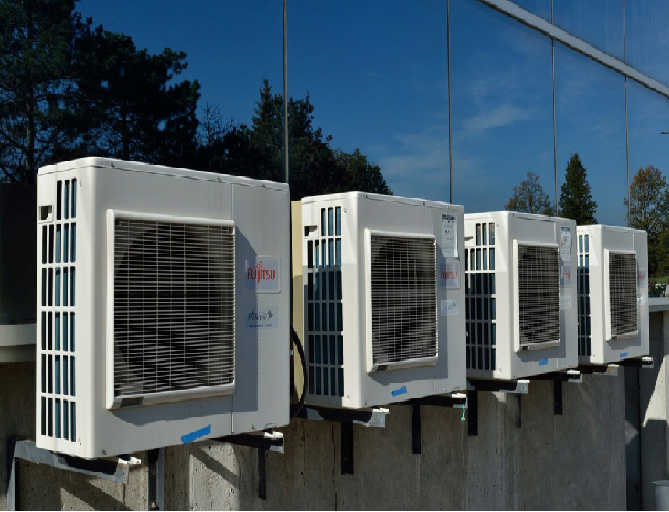
What is HVAC?
HVAC is a general term that refers to heating, ventilation and air conditioning services, usually found in a building. Sometimes HVAC can also be referring to refrigeration as well. HVAC services usually regulate the temperature, humidity, and the air quality found within a building.
Temperature
HVAC systems can operate independently, or be part of a larger network of equipment that operates to maintain a consistent temperature with heating and cooling as required. Water can be heated to power radiators, or underfloor heating. Sometimes these systems are powered by steam. Energy can also be used, with coolant to chill water or lower temperatures with air conditioning. Heating and cooling systems both make use of heat transfer via coils to reduce or raise the ambient temperature.
Humidity and condensation
Humidity levels are essentially determined by the amount of water that is available in the atmosphere. This can be important because when air holds less water, the result can be condensation. Often when air is chilled, it contains less water, leading to condensation, and then dehumidification may be required.
Image Credit
Regulation of humidity is generally achieved by changing ventilation levels, and dehumidification. If the atmosphere is too dry, then humidification may be needed. For more on the science behind humidity, see this report in The Guardian.
In commercial buildings, HVAC services are frequently provided in the form of AHU, or air handling units. These are usually connected to a series of ducts that enables air to be added or extracted from internal spaces.
If you want to find out more about how to install or use a spiral duct and what part it plays in HVAC systems, then the first step should be to contact experts in this area, such as A reputable company should be able to provide all the information you require about obtaining, maintaining or installing a spiral duct.
When designing an HVAC system, it is necessary to look at the entire operation, even when it is made up of independently operating units. All parts of the system need to interact with each other intelligently and efficiently to ensure that heating, cooling, humidity and air quality are provided at satisfactory and consistent levels. The system can become even more complicated when other factors, such as sustainable energy from solar panels or extreme weather, are added in.